Greenhouse lighting supply
Providing the required light in the greenhouse
Optical balance point
Optical saturation point
Light quality
Supplementary lighting supply
Providing the required light in the greenhouse
Light: Solar energy is involved in all plant structures and the end result of these processes is plant growth, which leads to an increase in dry matter. In the event that all factors, including the amount of carbon dioxide, temperature and humidity are optimal. To perform photosynthesis, light intensity is needed at the desired level. Low light reduces photosynthesis and plant growth and more light causes damage to chloroplasts and reduces photosynthesis.Photoperiod is the time of day when light shines on a plant. The length of the day varies depending on the season and latitude. In the Northern Hemisphere, day length is especially important four days a year.
April 1: March, when the sun is directly above the equator, and on this day the length of day and night is equal to 12 hours. And it is called spring equinox.
June 21 (June 21): The sun rises to the northernmost part of the equator and is the longest day and shortest night of the year and is called the summer solstice.
September 30 (September 21): When the sun is directly above the equator and the length of day and night are equal and is called the autumnal equinox.
30 Azar (December 21): when the sun is in the southernmost part below the equator and is the shortest day and the longest night of the year and is called the winter solstice (Yalda night)
Optical balance point
Light compensation point: It is the point where the intensity of photosynthesis is equal to the intensity of respiration. At this point all the materials produced in photosynthesis are consumed in respiration. The light balance point in sun-loving plants is higher than that of shade-loving plants.
Optical saturation point
Light saturation point: The point at which photosynthesis is maximal and photosynthesis does not increase with increasing light is called the optical saturation point.
Light quality
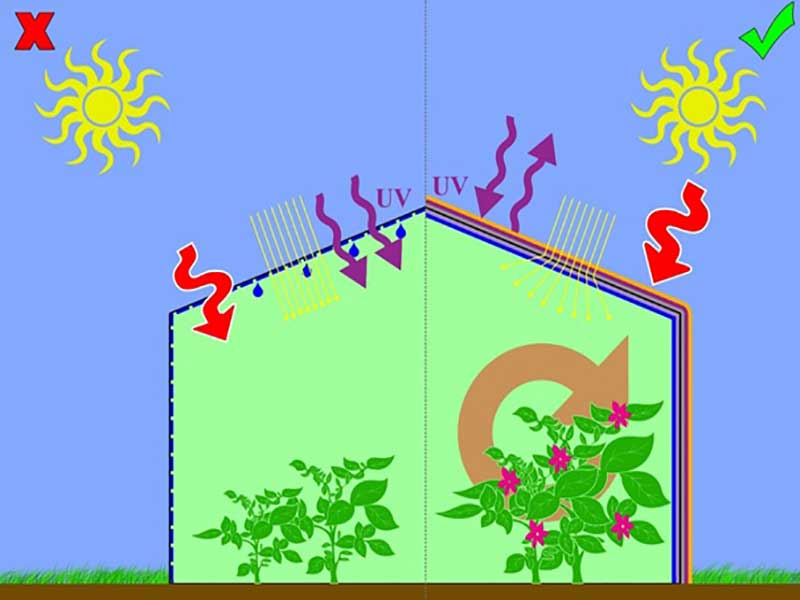
Light quality: Ultraviolet rays with a wavelength of 400-300 nm cause damage to the plant and are invisible to the human eye. Infrared rays with a wavelength of 750-700 nm are outside the human sense of sight and are essential for plant growth but have no effect on plant photosynthesis. Optical spectrum (760-380 nm) is involved in photosynthesis. The amount of photosynthesis in red and blue light is maximum. If the plant is only exposed to blue light, the growth will decrease and the plant organs will become stiff and dark, and if the plant is exposed to red light, the plant growth will increase and the plant organs will become soft and delicate.All light wavelengths are required for photosynthesis. Increased light intensity: With the exception of shade-loving, increasing light in mid-autumn to early spring increases yield. The simplicity of the glass frames on the greenhouse increases the capacity of the frames and the width of the frames increases the intensity of the light entering the greenhouse. The wooden frame significantly reduces the light intensity, and it is better to paint the wooden frame with white so that it reflects instead of absorbing light. It is also better to paint the glass frames of the greenhouse white and the outer cover of the frames to be painted once every two years and the inside once every 5 years.The reduction of light emitted to the greenhouse is: 10% by the frame and 5% by the glass frame and 7% of the glass and 78% of the light enters the greenhouse. Glass should be cleaned in autumn and winter of materials that have been painted to reduce the intensity of incoming light. These materials reduce the amount of incoming light by about 20%.
Supplementary lighting supply
Types of lamps
White light (contains inflamed tungsten filament): The light in these lamps has high heat output and low light quality, and the efficiency of converting electrical energy into light is 7%. More is converted to heat.
Fluorescent lamps: These lamps are effective in growth and development. The disadvantage of these lamps is the low voltage power and it is necessary to consume a large number of lamps, in which case the high cost of wiring and installation will cause shadows on the plants. Cold and warm incandescent bulbs are very effective (20%) and are the most common and most common fluorescent bulbs for plant growth. The light in these lamps is close to blue light.
High pressure sodium lamps: These lamps are cheap and easy to use. The conversion efficiency of electrical energy to light is about 20%.
Radiation time is 18-16 hours (natural and complementary light). Supplementary lamps are off when the natural sunlight is fully lit. At this time the light should be twice the complementary light of the lamps. 24-hour radiation is harmful or ineffective for most plants. The reaction of plants in the young stage (transplant stage in the nursery or seedling box) is high and decreases in intensity over time.For a planting bed 1.2 m wide, a 60-watt bulb at a distance of 1.2 m from each other at a height of 1.5 m above the soil surface, and for two beds a 100-watt bulb at a distance of 1.8 m from each other at a height of less than 1.8 meters required. 16 watts of light are needed to illuminate each square meter of greenhouse area.